The example app's user interface for creating a new book record looks as in Figure 9.3 below.
Figure 9.3. The user interface for creating a new book record with ISBN, title and four enumeration attributes
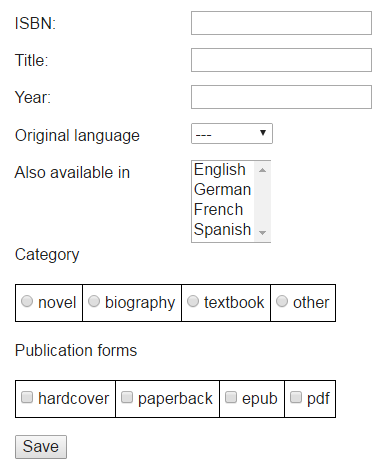
We use JSF selection lists for rendering the enumeration attributes
originalLanguage and otherAvailableLanguages. The affected files are
WebContent/views/books/create.xhtml and
WebContent/views/books/update.xhtml:
<ui:composition template="/WEB-INF/templates/page.xhtml">
<ui:define name="content">
<h:form id="createBookForm" styleClass="pure-form pure-form-aligned">
<h:panelGrid columns="3">
...
<h:outputLabel for="originalLanguage" value="Original language " />
<h:selectOneMenu id="originalLanguage" value="#{book.originalLanguage}">
<f:selectItem itemValue="" itemLabel="---" />
<f:selectItems value="#{book.languageItems}" />
</h:selectOneMenu>
<h:message id="originalLanguageMessages" for="originalLanguage" errorClass="error" />
<h:outputLabel for="otherAvailableLanguages" value="Other available languages " />
<h:selectManyListbox id="otherAvailableLanguages" value="#{book.otherAvailableLanguages}">
<f:selectItems value="#{book.languageItems}" />
</h:selectManyListbox>
<h:message id="otherAvailableLanguagesMessages" for="otherAvailableLanguages" errorClass="error" />
...
</h:panelGrid>
...
</h:form>
</ui:define>
</ui:composition>The JSF h:selectOneMenu allows to create single selection lists. The rendered
view uses the HTML5 select element. The list is auto-populated with the
existing language items, as result of using <f:selectItems
value="#{book.languageItems}"/>. The JSF expression
#{book.languageItems} results in calling a method named
getLanguageItems of the Book instance (a getter for the
specified attribute). Notice that it is not mandatory to define the
languageItems attribute in the JavaBean class Book (and in our
case this attribute is not even needed), but we need to define a method named
getLanguageItems. This method returns a set of SelectItem
elements which are used to populate our selection list. The corresponding method code is
shown below:
public SelectItem[] getLanguageItems() { SelectItem[] items = new SelectItem[LanguageEL.values().length]; int i = 0; for ( LanguageEL lang : LanguageEL.values()) { items[i++] = new SelectItem( lang.name(), lang.getLabel()); } return items; }
For the multiple selection list, the h:selectManyListbox JSF element is
used. It uses the same getLanguageItems method to obtain the values used to
populate the list. The corresponding rendered HTML5 code uses the select
element with the multiple attribute set, i.e., <select
multiple="multiple" .../>.
Since the enumeration attributes category and publicationForms
have not more than seven possible values, we can use a radio button
group and a checkbox group for rendering
them:
<ui:composition template="/WEB-INF/templates/page.xhtml">
<ui:define name="content">
<h:form id="createBookForm" styleClass="pure-form pure-form-aligned">
<h:panelGrid columns="3">
...
<h:outputLabel for="category" value="Category" />
<h:selectOneRadio id="category" value="#{book.category}">
<f:selectItems value="#{book.categoryItems}" />
</h:selectOneRadio >
<h:message id="categoryMessages" for="category" errorClass="error" />
<h:outputLabel for="publicationForms" value="Publication forms " />
<h:selectManyCheckbox id="publicationForms" value="#{book.publicationForms}">
<f:selectItems value="#{book.publicationFormsItems}" />
</h:selectManyCheckbox>
<h:message id="publicationFormsMessages" for="publicationForms" errorClass="error" />
</h:panelGrid>
...
</h:form>
</ui:define>
</ui:composition>The radio button group is obtained by using the h:selectOneRadio JSF
element. It renders in HTML5 as a set of <input type="radio" name="groupName" ...
/> elements. Using the same technique as for selection lists, the group of radio
buttons is created with the help of a set of SelectItem objects, which contains
the required data. The corresponding getCategoryItems method from the
Book class has a very similar code as getLanguageItems
one.
The checkbox group is created by using the h:selectManyCheckbox JSF
element, and populated in the same way as for the category attribute case, by
using a getPublicationFormsItems. The resulting HTML5 code uses
<input type="checkbox" ... /> elements.
As for all the other properties, the JPA annotations are responsible for validation and
creation of custom error messages. For example, in the case of publicationForms
attribute, we have the following code:
@Convert( converter = pl.model.converter.PublicationFormsConverter.class) @Size( min = 1, message = "At least one publication forms is required!") private Set<PublicationFormEL> publicationForms;
While the @Convert annotation is not used for validation but rather is
responsible for the serialization and deserialization tasks, the @Size
annotation with a min = 1 parameter enforce to have at least one element in
multivalued publicationForms attribute, otherwise the custom message defined by
using the message = "At least one publication forms is required!" annotation
property is shown as an error in the corresponding HTML5 view.